CUET UG Social Media
Cyber crime has emerged as a new breed of criminal activity in our interconnected world, where technology plays a significant role in our lives. This digital menace poses a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and even nations. It is important to have a good understanding of the different types of cyber crime, their effects, and the steps we can take to safeguard ourselves as we navigate the vast internet landscape. This article provides a thorough exploration of cyber crime, with a specific emphasis on its presence in India.
What is Cyber Crime?
Cyber crime involves criminal activities conducted through computers, networks, or the Internet. These offences can range from financial fraud and identity theft to cyberbullying and online stalking. As our dependence on digital technology grows, so does the sophistication and frequency of cyber crimes.
In India, the Information Technology Act of 2000 (amended in 2008) provides the legal framework for addressing cyber crimes. This legislation clearly outlines different cyber offences and the corresponding punishments for those responsible. Nevertheless, the ever-changing landscape of technology often poses challenges for the legal system in addressing emerging cyber crimes.
Now, let’s explore some of the most prevalent types of cyber crime in India and around the world.
Online Frauds

One of the most common and financially damaging forms of cyber crime is online fraud. These deceptive schemes aim to fool innocent individuals into giving away their money or sensitive information. In India, the complexity of online fraud has increased, with individuals from various backgrounds being targeted.
Common Types of Online Frauds
- Phishing Scams: Fraudsters create fake websites or send deceptive emails that mimic legitimate businesses to steal personal information. For example, a victim might receive an email that appears to be from their bank, asking them to “verify” their account details.
- E-commerce Fraud: With the rise of online shopping, scammers have found new ways to exploit buyers and sellers. This can include non-delivery of goods, selling counterfeit products, or using stolen credit card information to make purchases.
- Investment Scams: Fraudsters attract victims with promises of high returns on investments in cryptocurrencies, stocks, or other financial instruments. These schemes often collapse, leaving investors with significant losses.
- Job Scams: Unemployed individuals are targeted with fake job offers that require them to pay for “training” or “registration fees.”
Real-life Example: The Jamtara Scams
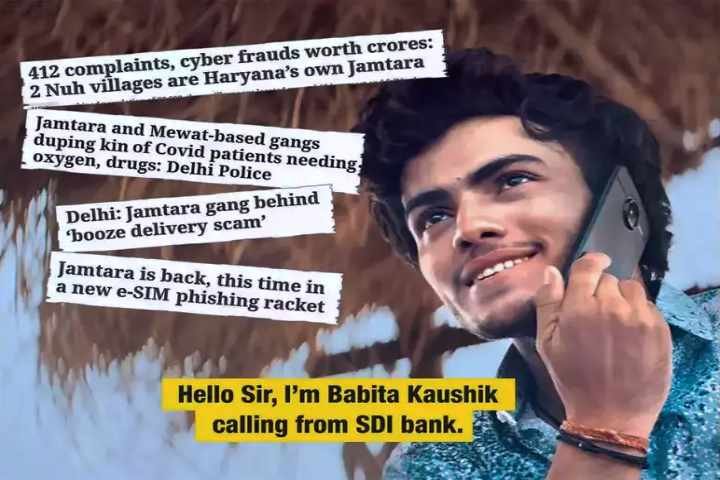
One of the most infamous cases of online fraud in India originated from the Jamtara district in Jharkhand. Young scammers from this area became notorious for their phishing operations, duping people across the country out of millions of rupees. Their modus operandi involved calling victims while posing as bank officials and tricking them into revealing their account details or OTPs (One-Time Passwords).
The Jamtara scams gained such notoriety that they inspired a popular Netflix series highlighting the growing problem of cyber crime in India. This case underscores the need for increased public awareness and vigilance.
Protecting Yourself from Online Frauds
1. Be skeptical of unsolicited emails, messages, or calls asking for personal information.
2. Use strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts.
3. Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
4. Regularly monitor your bank statements and credit reports for any suspicious activity.
5. Verify the legitimacy of websites before making online purchases or entering sensitive information.
Online Bullying
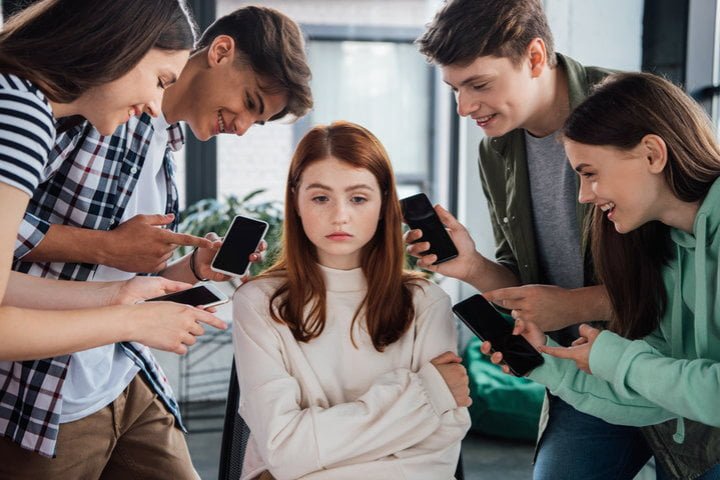

As social media platforms have become an integral part of our lives, they’ve also given rise to a new form of harassment: online bullying. Such behavior can cause significant psychological harm to victims, particularly young individuals.
Understanding Online Bullying
Online bullying, also known as cyberbullying, involves using digital platforms to harass, threaten, or embarrass others. It can take many forms, including:
1. Sending messages that are rude or contain threats
2. Sharing inaccurate or misleading information online
3. Sharing embarrassing photos or videos without consent
4. Creating fake profiles to imitate or mock someone
5. Excluding someone from online groups or activities
In India, online bullying has become a significant concern, particularly among school and college students. A 2022 survey report, “Cyberbullying in Plain Sight,” by McAfee, found that children worldwide suffer racially motivated cyberbullying. According to parents, 45% of boys aged 10 to 14 and 41% of girls aged 10 to 14 in India found themselves the victims of such cyberbullying.
Case Study: The Blue Whale Challenge

While not a traditional form of cyberbullying, the Blue Whale Challenge that swept across India in 2017 demonstrates the potential dangers of online manipulation. This “game” involved a series of tasks given to participants, resulting in self-harm or suicide. Several deaths in India were linked to this challenge, prompting authorities to take action and raise awareness about the dark side of online interactions.
Combating Online Bullying
- Education: Schools and parents should educate children about responsible online behavior and the consequences of cyberbullying.
- Reporting Mechanisms: Social media platforms need to have robust reporting systems for bullying and harassment.
- Legal Framework: India has introduced specific provisions in Sections 66 and 67 of the Information Technology Act 2000 to address cyberbullying, but enforcement remains a challenge.
- Support Systems: Creating helplines and counseling services for victims of online bullying is crucial.
It is crucial to speak up and seek help if you are a victim of online bullying. Don’t suffer in silence.
Stalking: The Digital Shadow

Stalking has taken on a new dimension in the digital age. Cyberstalking involves using technology to harass, intimidate, or monitor someone without their consent. This can include constantly messaging someone, tracking their online activities, or using GPS to monitor their physical location.
Forms of Cyberstalking
- Social Media Stalking: Constantly monitoring someone’s social media profiles, liking or commenting on old posts, or creating fake profiles to interact with the victim.
- Email harassment: Sending repeated, unwanted emails or using email to threaten or intimidate the victim.
- GPS Tracking: Using smartphone apps or GPS devices to track someone’s physical location without their knowledge.
- Catfishing: Creating a fake online persona to build a relationship with the victim, often for manipulative purposes.
In India, cyberstalking has become a growing concern, particularly for women. A 2017 Norton Cyber Security Insights Report found that in 2016–17, more than 186.44 million adults in India experienced cybercrime, and they lost $18.5 billion collectively.
Legal Protections Against Cyberstalking in India
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Information Technology Act provide legal recourse for victims of cyberstalking:
1. Section 354D of the IPC specifically criminalizes stalking, including electronic surveillance.
2. Section 66E of the IT Act deals with violations of privacy.
3. Section 67 of the IT Act addresses the transmission of obscene material in electronic form.
Protecting Yourself from Cyberstalking
1. Be cautious about sharing personal information online.
2. Regularly review and update your privacy settings on social media platforms.
3. Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
4. Be wary of accepting friend requests or messages from unknown individuals.
5. If you feel you’re being stalked, document all incidents and report them to the authorities.
Trolling: The Art of Digital Provocation

Trolling is a form of online behavior that aims to provoke emotional responses or disrupt normal discussions. Trolling, although initially perceived as harmless mischief, has the potential to escalate into more severe forms of harassment or cyberbullying.
Types of Trolling
- Flame trolling: Posting inflammatory messages to provoke emotional responses.
- Political trolling: Deliberately posting controversial political content to spark arguments.
- Grief trolling: Mocking or harassing people who are mourning or discussing sensitive topics.
- Concern trolling: Pretending to be supportive while subtly undermining or criticizing.
In India, trolling has become a significant issue, particularly in the realm of politics and celebrity culture. Public figures often face intense trolling campaigns, which can have real-world consequences.
Case Study: Sushant Singh Rajput and Online Trolling
The tragic death of Bollywood actor Sushant Singh Rajput in 2020 led to an unprecedented wave of online trolling. Various individuals, including other actors and filmmakers, were targeted with hate messages and threats. This case highlighted the toxic nature of online discourse and the need for more responsible social media usage.
Combating Trolling
- Don’t Feed the Trolls: Engaging with trolls often encourages their behavior. It’s usually best to ignore them.
- Use Moderation Tools: Many platforms offer tools to filter comments or block problematic users.
- Report Serious Incidents: If trolling escalates to harassment or threats, report it to the platform and, if necessary, to law enforcement.
- Promote Digital Literacy: Educating users about responsible online behavior can help create a more positive digital environment.
The Fight Against Cyber Crime: Resources and Reporting
As cyber crime continues to evolve, individuals and organizations must stay informed and know how to report incidents. In India, several resources are available to help combat cyber crime:
Cyber Crime Complaint Process
- Online Reporting: The Indian government has launched a dedicated portal (cybercrime.gov.in) for reporting cyber crimes. This allows citizens to file complaints online and track their status.
- Cyber Crime Police Stations: Many cities in India now have specialized cyber crime police stations. These units are equipped to handle digital investigations and cyber crime complaints.
- Helpline Numbers:
- Women Helpline: 1091
- Child Helpline: 1098
- Online Financial Fraud: 1930
Tips for Reporting Cyber Crime
- Act quickly: The sooner you report a cyber crime, the better the chances of resolving it.
- Preserve evidence: Save emails, messages, or screenshots related to the incident.
- Provide detailed information: The more information you can provide, the easier it will be for authorities to investigate.
- Follow up: Use the provided complaint number to track the status of your case.
Cyber Crime Punishment in India
The punishment for cyber crimes in India varies depending on the nature and severity of the offense. Some key provisions include:
- Hacking and Data Theft: Imprisonment of up to 3 years and/or a fine of up to ₹5 lakhs (Section 66 of IT Act)
- Identity Theft: Imprisonment up to 3 years and fine up to ₹1 lakh (Section 66C of IT Act).
- Cyberstalking: Imprisonment of up to 3 years and a fine (Section 354D of the IPC).
- Publishing or transmitting obscene material: imprisonment for up to 3 years and a fine of up to ₹5 lakhs (Section 67 of the IT Act).
It’s worth noting that these punishments can be enhanced for repeat offenders or in cases involving more serious crimes.
The Future of Cyber Crime: Emerging Threats and Challenges
As technology continues to advance, new forms of cyber crime are likely to emerge. Some areas of concern include:
- AI-powered Attacks: Artificial intelligence could be used to create more sophisticated phishing scams or deepfake videos for fraud or blackmail.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: As more devices become connected to the internet, they could become targets for hackers.
- Cryptocurrency Scams: The growing popularity of digital currencies presents new opportunities for fraudsters.
- 5G and New Attack Vectors: The rollout of 5G networks may create new vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit.
Conclusion: Staying Safe in the Digital World
Cybercrime is a complex and ever-evolving threat that requires constant vigilance. By understanding the various forms of cyber crime, staying informed about emerging threats, and knowing how to report incidents, we can all help create a safer digital environment.
Remember these key points:
1. Stay informed about different types of cyber crimes and how to protect yourself.
2. Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
3. Be cautious about sharing personal information online.
4. Report any suspicious activities or cyber crimes to the appropriate authorities.
5. Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity practices and technologies.
Together, we can fight cybercrime and make sure that the internet is still a place for growth, innovation, and communication rather than a haven for lawbreakers. We can do this by encouraging responsible online behavior.
The CUET UG Mass Communication syllabus contains this topic under the Social Media section.







