CUET UG Social Movements
Caste Movements: Dalit Panther Movement 1972
The social movements in India go beyond demonstrations; they represent a nation’s demand for progress, equality, and justice. The social movement in India is a significant part of the country’s rich history.
The following is a list of some of India’s most well-known social movements and their effects on societal advancement and cultural change:
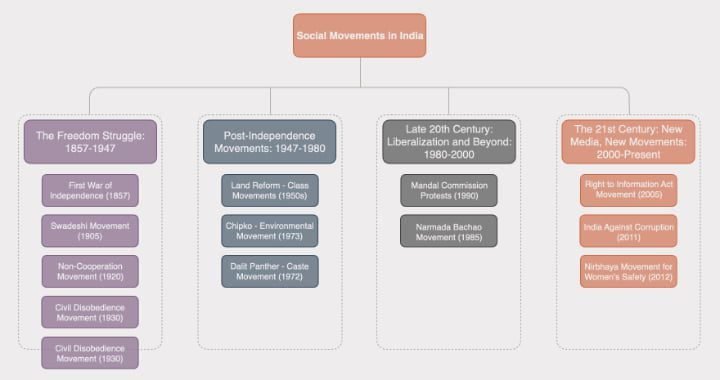
- The Freedom Struggle: 1857–1947
- Post-Independence Movements: 1947–1980
- Late 20th Century: Liberalization and Beyond: 1980–2000
- The 21st Century: New Media, New Movements: 2000-Present
This article will discuss the Dalit Panther Movement, which was a caste movement and a significant contributor to India’s post-independence movements (1947–1980), which led to societal transformation.
The caste system is a fundamental aspect of India’s social structure and has been a key area for resistance and reform efforts. Several movements have emerged, advocating for the rights and respect of oppressed castes. The Dalit Panther Movement, which was established to take assertive action against caste-based atrocities, was born out of this need.
The Genesis of the Dalit Panther Movement
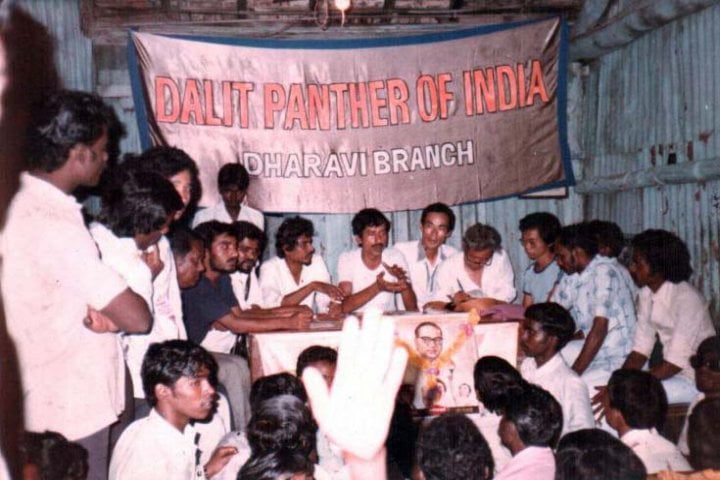

The word Dalit is commonly used for the poor and oppressed. There has not been a single, unified Dalit movement in the country. Different movements have highlighted different issues related to Dalits and around different ideologies.
However, there has been a common quest for equality, self-dignity, and the eradication of untouchability. A growing body of Dalit literature has accompanied this.
Dalit Panther is considered India’s first aggressive Dalit Youth Movement, which started as a reaction to the atrocities against Dalits in Maharashtra in 1972. The Black Panther movement in the USA served as its inspiration.
The Stalwarts of the Dalit Panther Movement
Dalit Panther was established as a Dalit youth organization by J.V. Pawar, Namdev Dhasal, and Raja Dhale. Dhasal was a rebel Marathi poet. With his provocative poems, such as Golpitha, he managed to garner attention across India. Raja Dhale was an author who was known to be articulate and intellectual.

His regularly published articles in the Marathi weekly Sadhana stirred the conscience of many and started a completely new debate in Maharashtra. He asked what is the use of this ‘freedom’ for him or lakhs like him? “What is to be done with this tricolor?” he questioned in his article, pointing to the lack of improvement in the lives of Dalits despite 25 years of independence.

This was the first literate generation of Dalits after Dr Ambedkar, who wanted to stand against discrimination and the lack of Dalit and tribal seats in government jobs.
Impact and Legacy of the Dalit Panther Movement
The Dalit Panther Movement was more than just a political movement; it sparked a cultural revolution by questioning the dominant narrative through literature, poetry, and theatre. Despite facing internal conflicts, its impact remains strong, motivating future generations of Dalit leaders and shaping the course of Indian politics.
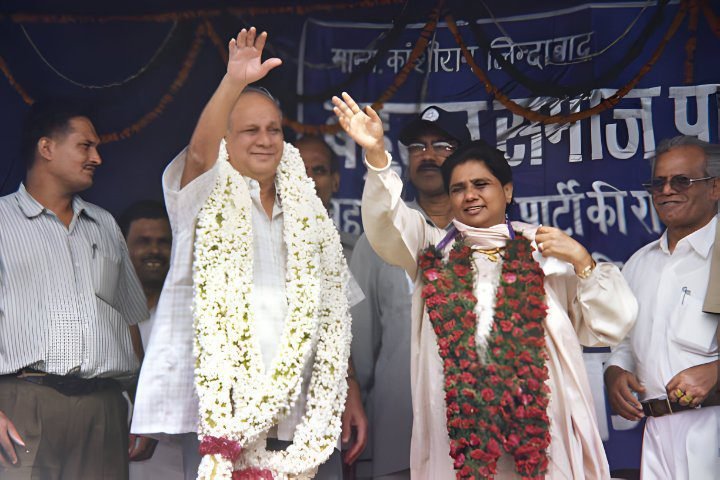

Dalit Panther came up with a manifesto against the capitalist powers. The impact of Dalit Panther on the national political and social landscape is immense. The Dalit Panther inspired Kashiram, founder of the Bahujan Samaj Party, who elevated Dalit politics in North India.
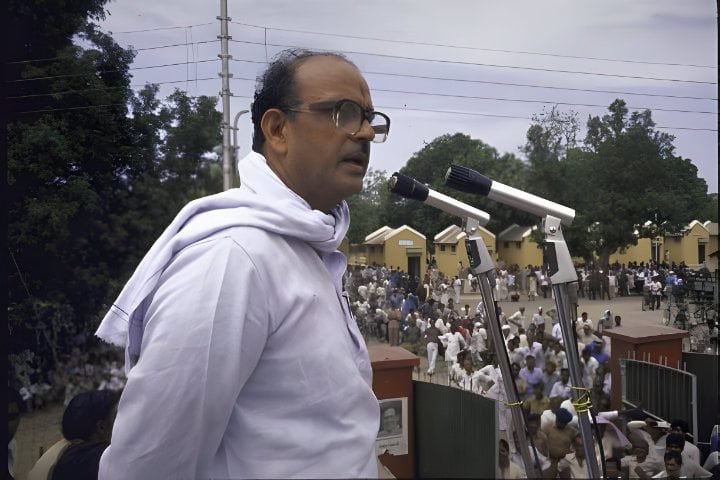
By 1977, differences in Dalit Panther emerged and manifested on various levels. A prominent face of the movement, Ramdas Athavale, Minister of State for Social Justice and Empowerment of India, and his supporters, started ‘Bharatiya Dalit Panther’ in the same year. In 1999, he founded the Republican Party of India (Athawale).

According to the political analyst, the Dalit Panthers carved out a place for themselves in the sociocultural and political spheres. Primarily, it was a political movement; however, its leaders understood their cultural responsibilities well.
The Dalit Panther Movement is a significant part of India’s history in the fight for social justice. Its principles of resistance, resilience, and cultural assertion still serve as an inspiration to marginalized communities, highlighting the importance of collective action in creating a more equitable society.
The CUET UG Mass Communication syllabus contains this topic under the Communication section.