CUET UG Advertising
Advertising Concepts and Process: Introduction
A business offers its product(s) or services to buyers through a marketplace. A market refers to an arrangement where buyers and sellers (businesses) come in contact, directly or indirectly, to buy or sell a product or a service.
However, developing a product or service is a long-term and ongoing process.
The first step in developing the product or service is conducting thorough research and analysis to gain insights into market trends, consumer preferences, and the competitive landscape.

The steps involve:
- Market Research: Gathering industry trends, customer behavior, and market dynamics information.
- Consumer Analysis: Understanding target customers’ needs, wants, and pain points.
- Competitor Research: Analyzing competitors’ strategies and positioning to identify opportunities and differentiate the product.
Then, the Research and Development (R&D) business department finalizes the product/service by defining its form, specifications, conditions, look, appearance, packaging and USP (the unique selling point).
All the mentioned steps are about defining the identity of the product.

Market research also gives a projection to the targeted buyer regarding their socio-economic profile, how the product will be positioned to appeal to the targeted buyers, what the selling strategy should be, etc.
The process of advertising is an extension of this strategy. Advertising is about giving a product a personality/identity through persuasive communication.
Persuasive communication is the core of advertising. It is the art of crafting messages to influence people’s attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors. It’s about strategically using language, visuals, and emotions to convince targeted buyers of a particular point of view or to take a specific action.
What is Advertising?
After carefully analyzing the market, when a business develops a product to satisfy market demand, there is a need to establish contact with the targeted buyers to sell that product.
Moreover, this has to be done through mass contact so that the product can get maximum exposure to many people.
The best way to reach the market is through mass communication, and advertising is one of the means of such mass communication, along with other means that may or may not use mass communication, like publicity, sales promotion, and public relations.
As a means of mass communication, advertising promotes the sale of goods, services, images, and ideas through information and persuasion. It is essential to understand that advertising alone cannot sell a product that is of poor quality, costly, or not up to the consumer’s expectations. Advertising only helps in selling.
Advertising Definition
Advertising is any paid form of non-personal controlled communication by an identified sponsor using mass media to persuade or influence an audience to sell ideas, goods, and services.
Paid form: Advertisers purchase time or space in mass media to communicate about a particular product or service.
Non-personal communication: It is done in a non-personal manner through mass media. Personal selling takes place when a personal face-to-face presentation is made.
Controlled: The word “controlled” distinguishes between advertising and personal selling or publicity. The advertiser controls the content, time, and direction of an advertising message.
An Identified Sponsor: Advertising discloses or identifies the source of the opinions and ideas it presents. This point distinguishes advertising from propaganda.
Idea, Goods, and Services: It is not only restricted to tangible goods.
Advertising is a tool of marketing that disseminates information about a product to a large number of people while using purchased space or time in various mass media.
However, it’s important to remember that businesses can’t do anything without a good product. No amount of advertising and marketing effort can sell the wrong product to all the customers all the time. Advertising success primarily depends on the customer satisfaction with the product.
Advertising Concept
Advertising messages are delivered through various media: television, radio, newspapers, magazines, billboards, direct-mail campaigns, the Internet, clothing lines with messages printed on them, telemarketing programs, and even messages heard while someone is on hold on the telephone. These are the numerous ways to attract potential customers.
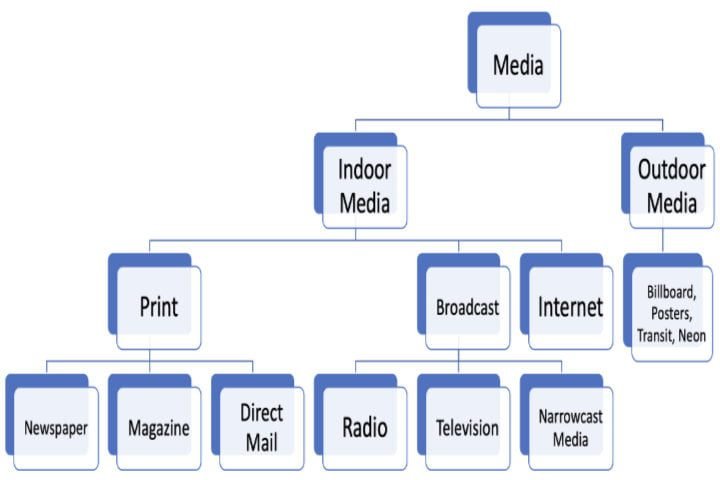
It is very difficult to prepare ads for every possible medium. Therefore, designing a message that must give an advantage in a highly cluttered world where customers are increasingly proficient at simply tuning ads out is a tremendous challenge.
Advertising intends to sell and create an aspiration towards a particular product and establish that vital and persuasive distinction that makes it a brand.
A brand is a sign of identity—the mark or label differentiating one product from another. A product acquires a particular identity or feel and a specific brand value because of the kind of advertising that supports it.
Advertising Process
Market Segmentation
Buyers are not homogeneous; they differ widely on a demographic and geographic basis. Therefore, it is essential to offer products that suit the needs of the different buyers based on their age, gender, education level, income level, personal references, etc., as well as the type of geographical region in which they are based.
Market segmentation is the process of dividing the heterogeneous market into several sub-markets called segments, each of which tends to be homogeneous in most of the significant aspects.
Targeting
After segmentation, suitable products are decided to be offered to target buyers. The other important marketing tools, like price and distribution channels, are customized accordingly. This is called Targeted marketing.
Advertising Theme Identification
The advertisements are built around a core idea. This core idea runs through the entire advertising campaign, which consists of a series of advertisements. The core idea is thus the theme of the advertisement.
For example, the Liril soap advertisement is built around the concept of freshness.
The following themes usually occur in advertisements:
Utilitarian Theme

This theme focuses on showcasing a product’s practical benefits and usefulness. For example, Tide laundry detergent advertising emphasizes its ability to effectively remove stains and whiten clothes. The emphasis is on how the product fulfils a specific need or solves a consumer problem.
Focused Theme

This theme targets a specific segment of consumers or a niche market with tailored messaging. For instance, Johnson’s baby products are marketed specifically towards parents and caregivers of infants, highlighting features that cater to the needs of babies, such as gentle formulas and safety.
Informative Theme

This theme educates consumers about the product’s features, benefits, and advantages over competitors. It involves providing detailed information and sometimes making comparisons to help consumers make informed purchasing decisions. Informative advertising often focuses on facts and figures to build credibility and trust with the audience.
Projective Theme
This theme shifts the focus from the product to the advertiser or brand itself. Corporate ads often use projective themes to build brand image, reputation, and identity. These ads may highlight the company’s values, corporate social responsibility initiatives, or overall societal impact to create a positive consumer perception.
Achievement Theme

Advertisers showcase their accomplishments, milestones, or success stories in this theme to build credibility and trust with consumers. For example, an advertisement might highlight awards won, significant milestones achieved, or positive customer testimonials to demonstrate the brand’s credibility and track record of success.
Product Positioning Strategy
Positioning is a creative exercise that starts with a product but is more concerned with the buyer’s mind. The market is full of me-too products, with little differentiation. Also, the message is over-communicated as well. So, it is the responsibility of advertisers to make their products stand out in the minds of consumers.
The customer rates the products in their mind based on one or more criteria. The advertiser’s job is to get his product to the top of the list in some important way that makes people want to buy it.
The CUET UG Mass Communication syllabus contains this topic under the Advertising section.











